Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery via High-Throughput Screening
Creative Biolabs has built a team of experienced scientists with facilities and processes designed specifically to provide the best strategy and protocols to high-throughput screening services for potential antimicrobial peptides. We have successfully accomplished a number of projects and have delivered numerous novel or validated antimicrobial peptide targets in a range of therapeutic areas.
Introduction to High-throughput Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery
In the past few years, antibiotics have been widely used for treating various diseases caused by a large number of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. Meanwhile, many companies and groups are dedicated to discovering new antimicrobial peptides for drug development. As a result, a series of high-throughput assays have also been established to obtain meaningful data from peptides of interest. These assays usually can provide a rapid, large-scale screening for antimicrobial properties. For example, the surface localized antimicrobial display (SLAY) platform has been considered as a high-throughput screening assay for identifying novel antimicrobial peptides against gram-negative bacteria. In addition, high-throughput cell-based and luminescence-aided assays are also powerful tools for determining potential peptides against bacteria, such as pseudomonas aeruginosa. These assays can screen many candidate peptides at a fast-turnaround time and reveal the mechanism of action (MOA) of antibacterial activity in antibiotic discovery.
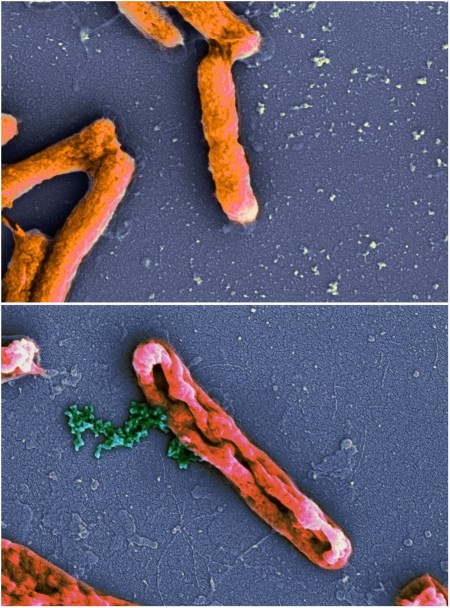 Fig. 1 Action of antimicrobial peptide on the cell membrane of E.coli. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig. 1 Action of antimicrobial peptide on the cell membrane of E.coli. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
High-throughput Screening Services for Antimicrobial Peptide
High-throughput screening for antimicrobial peptides has aroused much attention in the antibacterial drug discovery process. Pilot studies have suggested that these high-throughput screening approaches should provide a stable clone and the high peptide expression in different vectors. As a consequence, a variety of advanced techniques, including cell-based, fluorescence-based, as well as computer-aided, should be fully equipped to develop the sensitive antimicrobial peptide platform.
Currently, Creative Biolabs offers high-throughput antimicrobial peptide screening services for our worldwide customers to identifying their antimicrobial activity at different levels. In our company, Surface Localized Antimicrobial Display Platform has been generated based on numerous peptide libraries. Based on this platform, massive and high-quality data will be further analyzed to optimize peptide design and improve the peptide affinity. In addition, a fluorescence assay has also been generated to simultaneously detect the 96 peptide samples in a short time ( approximately 1-2 hours) and minimal cost.
With years of operational experience, Creative Biolabs is able to provide state-of-art services for any antimicrobial peptide discovery project. Our scientists specialized in drug discovery studies will work with you to develop a most appropriate strategy that will offer the reproducible data for your research. Now, we have developed efficient protocols for antibacterial drug discovery. And we can also conduct custom high-throughput peptide screening studies to meet any requirement of our clients. If you have any special needs in our target discovery services or be interested in learning more about our company, please feel free to contact us for more details.
For Research Use Only.
