The Dynamic Duo of Scientific Research: C57BL/6 vs BALB/c
In 1921, the researcher C.C.Little bred several inbred lines via Abby Lathrop mice, the male mice number 57 matched with the female mice number 52 to cultivate C57. The dark gray coat mice was cultivated into C57BL. BL is the abbreviation of "Black". In 1913, Halsey J. Bagg purchased a batch of albino mice from a pet merchant in Ohio. These mice are native to the wild European house mouse (Mus musculus) and are also called "Bagg Albino" because of a spontaneous mutation that results in an albino phenotype (tyrosinase gene Tyr mutation). Coincidentally, in 1920, Bagg's colleague E.C. MacDowell began to breed the inbred population through brother-sister mating. By 1923, the 26th generation had been reached, and a genetically stable inbred line was initially formed, named BALB (abbreviation of Bagg Albino). It was almost the same time as the birth of C57 mice, which can be said to be a deep fate. I'll introduce this dynamic duo by this article, giving you a deeper understanding of these two strains of mice.
Service you may interested in
Difference Between BALB/c and C57BL/6 Mice
From coat to genes
The most obvious difference between the two is the color of their fur. BALB/c mice are all white, that's because their tyrosinase gene (Tyr) has mutated, which makes their unable to synthesize melanin. After all, even the cleverest housewife can't cook a meal without rice. On the other hand, C57BL/6 mice have dark gray to black fur, which is regulated by the normally expressed Tyrp1 gene. In addition to the difference in fur color, there are also differences in the quality of the fur. C57BL/6 mice has a dense and elastic coat, black hair tips with dark grey tones, and no spontaneous hair loss. People with hair loss are very envious of this. However, BALB/c mice fur lacks luster, which mainly cause by fighting between female mice from different litters.
Eyes color
The eyes of 57BL/6 mice and BALB/c mice are like two completely different "optical instruments". C57BL/6 mice have dark irises, as if they have their own "light-proof filter" - this is due to the unique advantages of the retinal pigment epithelium: it can reduce light scattering and protect the retina like an antioxidant shield. However, due to the albino gene (Tyr mutation), BALB/c mice lack melanin in their irises, making their "ruby eyes" particularly eye-catching, but they also lack a layer of natural protection.
In terms of vision, BALB/c mice are more like "nearsighted players", with a vision of only 0.12 cyc/deg, which is much worse than the 0.39 cyc/deg of C57BL/6 mice; the clarity of seeing things (contrast sensitivity) is also slightly inferior, just like wearing a pair of glasses with inappropriate degrees, and everything you see has a "blurry filter" effect.
Body type difference
These two strain of mice also have differ in size. C57BL/6 mice are known as the "big guys in the mouse world." When they grow up, female mice weigh 20-25 grams, while male mice are even stronger, weighing 25-30 grams. Compared with BALB/c mice, the growth rate of C57BL/6 mice is almost like turning on the "accelerator", especially male mice, which are like teenagers who grow rapidly during puberty. Once they reach sexual maturity, their muscles are particularly obvious, and they have a strong sense of "tendon meat" all over their bodies, making them true "mouse fitness experts."
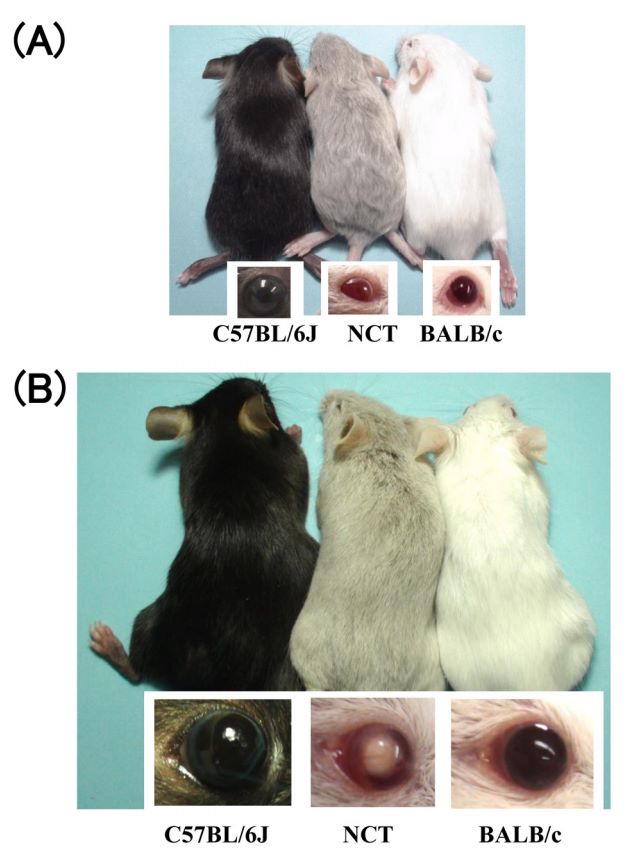 Fig.1 Image of C57BL/6J, NCT, and BALB/c mice at 2 weeks (A) and 12 weeks (B) of age.
Fig.1 Image of C57BL/6J, NCT, and BALB/c mice at 2 weeks (A) and 12 weeks (B) of age.
BALB/c and C57BL/6 Mice Immune Response
BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice are like partners with different personalities. They each have their own "specialties" in immune response, which is inseparable from their genetic background. BALB/c mice have the attribute of "humoral immunity expert". Because the MHC genotype is H-2d, they tend to "cultivate" Th2 type helper cells when presenting antigens, just like they are good at launching "antibody armies". Not only do they have high levels of natural antibodies, but they are also extremely sensitive to allergens and are prone to IgE-mediated allergic symptoms. For example, they can often be seen in asthma models. Its B cells are active and it is a classic host for the production of monoclonal antibodies. However, its cytotoxic T cells (CTL) are slightly weaker in combat power and rely more on antibodies to help fight viruses or tumors.
C57BL/6 mice are "cellular immune powerhouses". Their MHC genotype H-2b makes them better at activating Th1 immune responses, as if they have formed a "cell special forces team". They secrete a large number of cytokines such as IFN-γ, have strong CTL activity, and are more lethal to viral infections and tumor cells. They are almost a "golden model" in tumor immunotherapy research.When evaluating the efficacy of PD-1 antibodies, C57BL/6 mice are often an indispensable assistant. When invaded by bacteria or viruses, the macrophages in these mice are like ignited "flames" and are particularly prone to turning into "pro-inflammatory" (M1 type). They quickly release inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, triggering a strong inflammatory "storm", which is very similar to the pathogenesis of acute infection and autoimmune diseases. It is very suitable to use them to simulate experimental encephalomyelitis. Not only that, the NK cells of C57BL/6 mice can be called "anti-cancer guards" and are much more active than other mice. Once tumor cells are found, these NK cells will quickly attack and "encircle and suppress" tumor cells with efficient combat effectiveness, providing precious living samples for tumor research. Simply put, if you are studying allergies or antibody development, BALB/c is a more appropriate choice; if you focus on tumor immunity, viral infection or autoimmune disease, C57BL/6 is the "first choice". Both have their own strengths in immunology research and provide accurate model tools for exploration in different fields.
C57BL/6 Mice Advantages
C57BL/6 mice are like "all-around warriors" in scientific research. They are good at immunity, tissue research and biological clocks, and are particularly suitable for scenarios that require "strong firepower" cellular immunity and specific disease models. Their strong immunity mainly relies on powerful CD8+ T cells - these cells are like "anti-cancer special forces" in the body, which can accurately identify and eliminate abnormal cells. Therefore, scientists like to use them as "testers" when doing tumor immunotherapy experiments such as CAR-T therapy and PD-1 antibodies, and evaluate the treatment effect by observing how these cells get into the tumor and "cause damage". In addition, their immune system is particularly good at "fighting viruses" because the Th1 immune response is dominant and will secrete "anti-viral ammunition" such as IFN-γ and IL-2. When studying how influenza and herpes viruses are cleared, they can clearly see the process of CTL cells "charging forward", providing key clues for the development of vaccines and antiviral drugs.
In terms of simulating human diseases, the lungs and bones of C57BL/6 mice are the "best partners". Their lung tissue is naturally rich in collagen, with a flexible and elastic texture, like a sensitive "barometer" - when exposed to substances that are prone to pulmonary fibrosis, such as bleomycin and silica, they will quickly produce a stress response: fibroblasts are activated, and the lung matrix begins to accumulate. These pathological changes are almost identical to those in patients, making them the "golden model" for studying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Their bones are particularly sensitive to glucocorticoids, like a precise "balance". Once hormones are used, the dynamic balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts will be broken, which can directly show how hormones cause bone loss, avoiding interference caused by metabolic differences in other strains of mice, and is simply an ideal choice for studying the pathogenesis of osteoporosis.
BALB/c Mice Advantages
BALB/c mice are like "delicate players" in scientific research. They are naturally good at Th2-type immunity and metabolic adaptation, and are "right-hand men" in the study of allergies, parasitic infections, and circadian rhythm disorders. Their immune system is more inclined to the "humoral immunity route", and Th2 cells are as active as "conductors", allowing B cells to produce a large number of IgE and IgG1 antibodies. They are simply the "best protagonists" of allergy models: whether it is intestinal allergies caused by eating the wrong things, or barrier damage caused by skin allergies, they will have mast cells "releasing histamine" and serum IgE soaring, which are typical symptoms of human allergies. This advantage also comes in handy when encountering parasitic infections - to deal with "extracellular enemies" such as worms, antibodies are needed to "chase and intercept" with eosinophils and mast cells. The strong Th2 response of BALB/c is just "matching", and when developing malaria and schistosomiasis vaccines, it is more reliable to rely on them to evaluate the protective effect of antibodies.
In the study of metabolism and bone, BALB/c also have "unique skills": after long-term use of glucocorticoids, the fat cells in their bone marrow will "grow wildly", "squeezing out" the trabeculae, which is very similar to clinical glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis (such as femoral head necrosis), which may be related to the activation of the PPAR-γ pathway, and is a "living model" for studying bone fat metabolism imbalance. In addition, their biological clock is particularly "flexible". Even if the day and night are reversed every day (such as simulated shifts, jet lag), the biological clock gene can quickly "adjust the jet lag", which is suitable for studying how irregular work and rest can cause metabolic diseases, decreased immunity and other problems, and provides a flexible experimental subject for exploring the relationship between "biological clock and health".
Just as we said at the beginning, BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice are like the "Dynamic Duo" in scientific research. Each has its own unique skills: the former, with its strong cellular immunity and tissue sensitivity, "charges the front" in anti-cancer, anti-viral, and lung and bone disease models; the latter, with its excellent humoral immunity and metabolic adaptability, "delicately controls" in allergy, parasite, and circadian rhythm research. Although their immune system "personalities" are different (one prefers Th1, the other is good at Th2), they are both "outstanding" in their respective fields, and together provide all-round support for research in immunology, pathology, biological clocks, etc., from mechanism exploration to model construction.
If you want to learn more about the C57BL/6, please refer to:
References
- Shoji, Haruka, et al. "A nonsense nucleotide substitution in the oculocutaneous albinism II gene underlies the original pink-eyed dilution allele (Oca2p) in mice." Experimental animals 64.2 (2015): 171-179. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.14-0075
- Ma, Changxiao, et al. "Adaptive differences in cellular and Behavioral responses to circadian disruption between C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.19 (2024): 10404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910404
- Fransen, Floris, et al. "BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice differ in polyreactive IgA abundance, which impacts the generation of antigen-specific IgA and microbiota diversity." Immunity 43.3 (2015): 527-540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.011
- Hurdayal, Ramona, and Frank Brombacher. "Interleukin-4 receptor alpha: from innate to adaptive immunity in murine models of cutaneous leishmaniasis." Frontiers in immunology 8 (2017): 1354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01354
- Rojas-Ruiz, Andrés, et al. "Lung stiffness of C57BL/6 versus BALB/c mice." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 17481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-44797-x
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
