Popular Transgenic Mouse Models in Neuroscience and Immunology
In the era of precision medicine, transgenic mouse models have become a strategic resource for analyzing disease mechanisms and drug development. The need for pathological simulation of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Tauopathy in the field of neuroscience, and the urgency of studying T cell function and tumor immunity in the field of immunology have jointly promoted the innovation of transgenic technology. This article systematically sorts out the characteristics, application scenarios and latest breakthroughs of transgenic models related to neurodegenerative diseases and the immune system, providing a theoretical framework for interdisciplinary research design and clinical transformation.
Neurodegenerative Disease Models
5xFAD transgenic mice: an accelerated model of amyloid pathology
The 5xFAD model integrates five familial AD mutations (Sweden, Florida, and London mutations of the APP gene and M146L/L286V mutations of PSEN1) to achieve overexpression of Aβ42 driven by the Thy1 promoter. Its core advantage lies in the extreme acceleration of the pathological process: amyloid plaques can appear at 2 months of age, accompanied by neuroinflammation and microglial activation, and significant memory deficits appear at 6 months of age.
At the application level, this model has been successfully used to evaluate the efficacy of Aβ-targeted drugs, anti-inflammatory compounds (such as JNK inhibitors) and metabolic interventions (such as ketogenic diet). It is worth noting that female mice show more severe pathological phenotypes due to the high expression of the APP gene on the X chromosome, which requires that the experimental design must include sex as an independent variable.
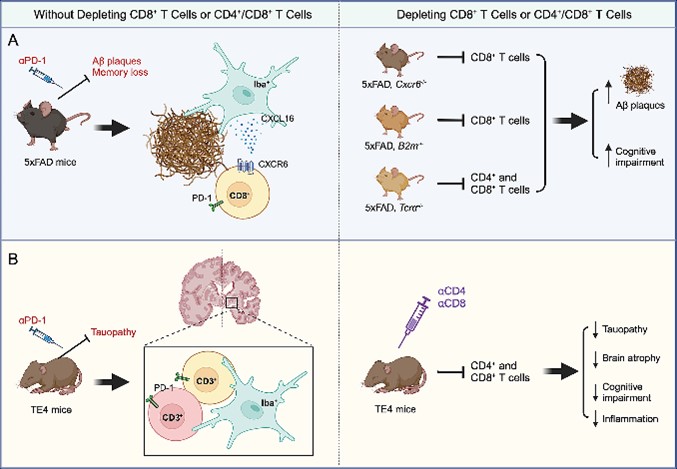 Fig. 1 Two distinct Alzheimer's disease mouse models. 1,2
Fig. 1 Two distinct Alzheimer's disease mouse models. 1,2
P301S Tau transgenic mouse: a core tool for tauopathies
The P301S Tau model is divided into two categories: the hTau.P301S model driven by the Thy1 promoter and the PS19 model driven by the Prnp promoter. The former has extensive deposition of phosphorylated Tau in the cortex, hippocampus and spinal cord, and motor disorders occur at 6 months of age; the latter has high expression of the 1N4R Tau isoform, and neuronal loss occurs at 9 months of age, which is closer to the temporal and spatial development of human Tau protein disease.
Studies have shown that this model can not only reveal the "prion-like transmission" mechanism of Tau oligomers through synaptic connections, but can also be used to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Tau vaccines (such as AADvac1) and autophagy activators (such as rapamycin). In 2023, Nature Neuroscience reported that antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeting Tau successfully reduced the pathological protein load by 50% in the PS19 model.
APP/PS1 double transgenic mice: a classic model of amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits
The APP/PS1 model simulates the Aβ deposition characteristics of early-onset AD through the combination of APPswe and PSEN1ΔE9 mutations. Its pathological process is mild and controllable: plaques appear at 6 months of age and cognitive decline occurs at 10-12 months of age, making it suitable for long-term intervention studies.
Recent studies have used this model to reveal the regulation mechanism of the gut-brain axis. For example, specific probiotics (such as Lactobacillus plantarum P-8) can reduce neuroinflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. In addition, the discovery that the traditional Chinese medicine compound Jiaotai Pill improves synaptic plasticity by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway was also verified based on this model.
Transgenic models of the immune system
The OT-1 model expresses specific TCRs that can recognize the ovalbumin (OVA) 257-264 peptide and H2-Kb complex, becoming the "gold standard" for studying T cell activation and tolerance. The model reveals that the MHC-peptide complex on the surface of dendritic cells (DCs) can be actively cleared by T cells through the "cleavage-internalization" mechanism, a discovery that revolutionizes the understanding of the dynamic balance of antigen presentation.
In vaccine development, the OT-1 model confirmed that nanoparticle carriers can increase the efficiency of antigen cross-presentation by more than 70%, providing a basis for the design of personalized tumor vaccines.
Pmel-1 TCR transgenic mice: the gold standard for melanoma immunotherapy
The Pmel-1 model targets the melanoma antigen gp100, and its adoptive T cell therapy (ACT) research directly promotes the optimization of clinical programs. For example, the combination of IL-2 and lymphocyte clearance can increase the tumor regression rate from 35% to 80%. In 2022, Cell reported that CD93 blocking antibodies increased the infiltration efficiency of Pmel-1 T cells by 3 times by remodeling tumor blood vessels, significantly prolonging survival.
Other TCR transgenic models: Diversifying tools for immune research
The influenza-specific TCR model revealed that the PD-1/TCF-1 axis regulates the molecular switch of T cell exhaustion, while the PLP-specific model successfully simulated the pathogenic mechanism of myelin-reactive T cells in multiple sclerosis (EAE). These models provide a precise platform for the study of infection immunity and autoimmune diseases.
Service you may interested in
Latest research progress and clinical translation potential
New discoveries in neurodegenerative disease models
In the study of neurodegenerative disease models, some new discoveries have emerged. Studies on the 5xFAD model have shown that ketone body intervention can improve cognitive function by regulating metabolism and neuroinflammation, providing a new metabolic intervention idea for the treatment of AD; studies on the P301S Tau model have shown that the small molecule drug Rapamycin can delay the progression of Tau pathology, providing a new drug candidate for the treatment of Tau protein disease; in addition, the combination of APP/PS1 and Tau models can simulate the full pathology of AD, promote the development of combination therapy, and provide a new strategy for a more comprehensive study of the pathogenesis and treatment of AD.
Breakthrough in clinical translation of immune models
Immune models have also made important breakthroughs in clinical transformation. Studies on the Pmel-1 model have shown that TCR gene editing combined with PD-L1 blockade can significantly inhibit melanoma metastasis, providing a new and effective solution for the clinical treatment of melanoma; the application of humanized models such as HLA-A2/NY-ESO-1 TCR mice has accelerated the evaluation of tumor vaccines and promoted the clinical transformation of tumor immunotherapy.
Transgenic mouse models are undergoing a paradigm shift from single pathology simulation to multi-system interaction research. CRISPR/Cas9 technology will promote the development of conditional induction models, and neuro-immune interactions (such as microglia-T cell interactions) have become new targets for interdisciplinary research. However, differences in immune microenvironments between species remain the main bottleneck for clinical translation. In the future, it is necessary to establish humanized organ chips and organoid co-culture systems to bridge the gap from animal models to clinical trials.
The development of this field requires not only technological innovation, but also relies on the construction of a data sharing platform - only through global collaboration can the translational medical value of transgenic models be maximized.
If you want to learn more about the transgenic mice, please refer to:
- What Are Transgenic Mice? Definition, Types, and Key Concepts
- Transgenic Mice in Cancer Research: From Tumor Models to Therapy Development
- How Are Transgenic Mice Created? Methods and Technologies
- Applications of Transgenic Mice in Disease Research and Drug Development
- Transgenic Mice vs Knockout Mice: Understanding the Differences and Research Benefits
- Humanized Transgenic Mice: Bridging Animal Models and Human Disease Studies
- Inducible and Conditional Transgenic Mice Tools for Controlled Gene Expression
- Advances in Genetic Engineering: CRISPR and BAC Technologies in Transgenic Mice
- Transgenic Reporter Mice: Tools for Visualizing Gene Expression
Creative Biolabs specializes in the custom generation of mouse models for a wide range of neurodegenerative and immune diseases, precisely tailored to meet your specific experimental requirements. Reach out to us today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise can accelerate your research.
References
- Hu, Dan, and Howard L. Weiner. "Unraveling the dual nature of brain CD8+ T cells in Alzheimer's disease." Molecular Neurodegeneration 19.1 (2024): 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-024-00706-y
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
